library(devtools) # to install ggvoronoi
library(ggvoronoi) # easy voronoi plotting with ggplot
library(palmerpenguins)
library(sf) # spatial data analysis tools helpful for voronoi
library(tidyverse)Voronoi Diagrams in R
Description of Voronoi Diagrams
A Voronoi diagram is a way of dividing space into regions based on distance to a specific set of points. Each region contains all the points that are closer to one particular point than to any other. These diagrams are useful in various fields such as geography, meteorology, and computer science for tasks like spatial analysis and resource allocation.
Install ggvoronoi from github as
It was removed from cran for some reason. You will need to install devtools first if you don’t have it.
# install.packages("devtools") # run this line if you don't have devtools installed
install_github("garretrc/ggvoronoi")Subset penguins data
d <- select(penguins, starts_with("bill"), species) |>
drop_na() |>
rename(x = bill_depth_mm, y = bill_length_mm) |>
distinct() first voronoi diagram
ggplot(d, aes(x,y)) +
stat_voronoi(geom="path") +
geom_point(aes(color = species))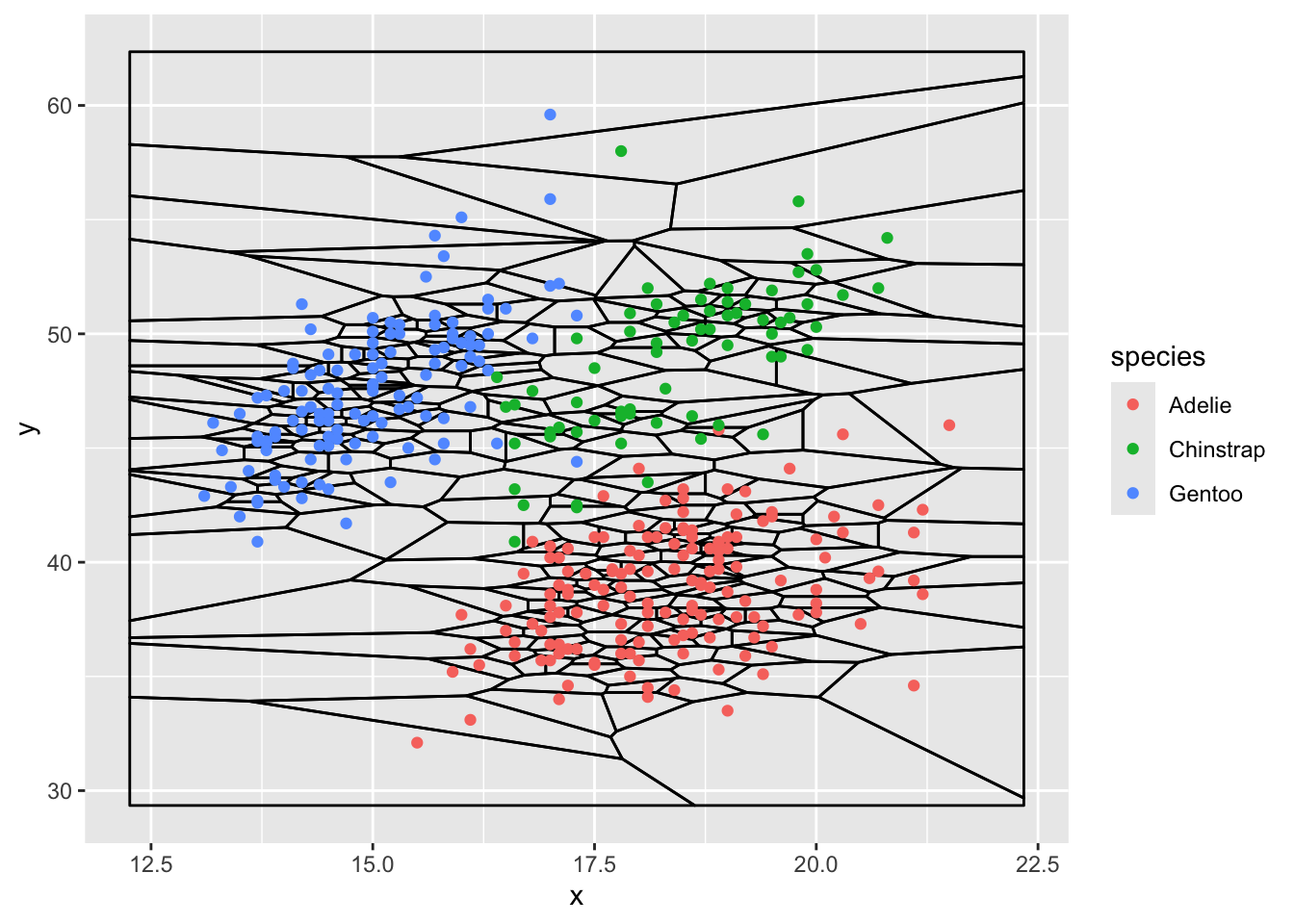
second voronoi diagram
ggplot(d) + geom_voronoi(aes(x,y,fill = species))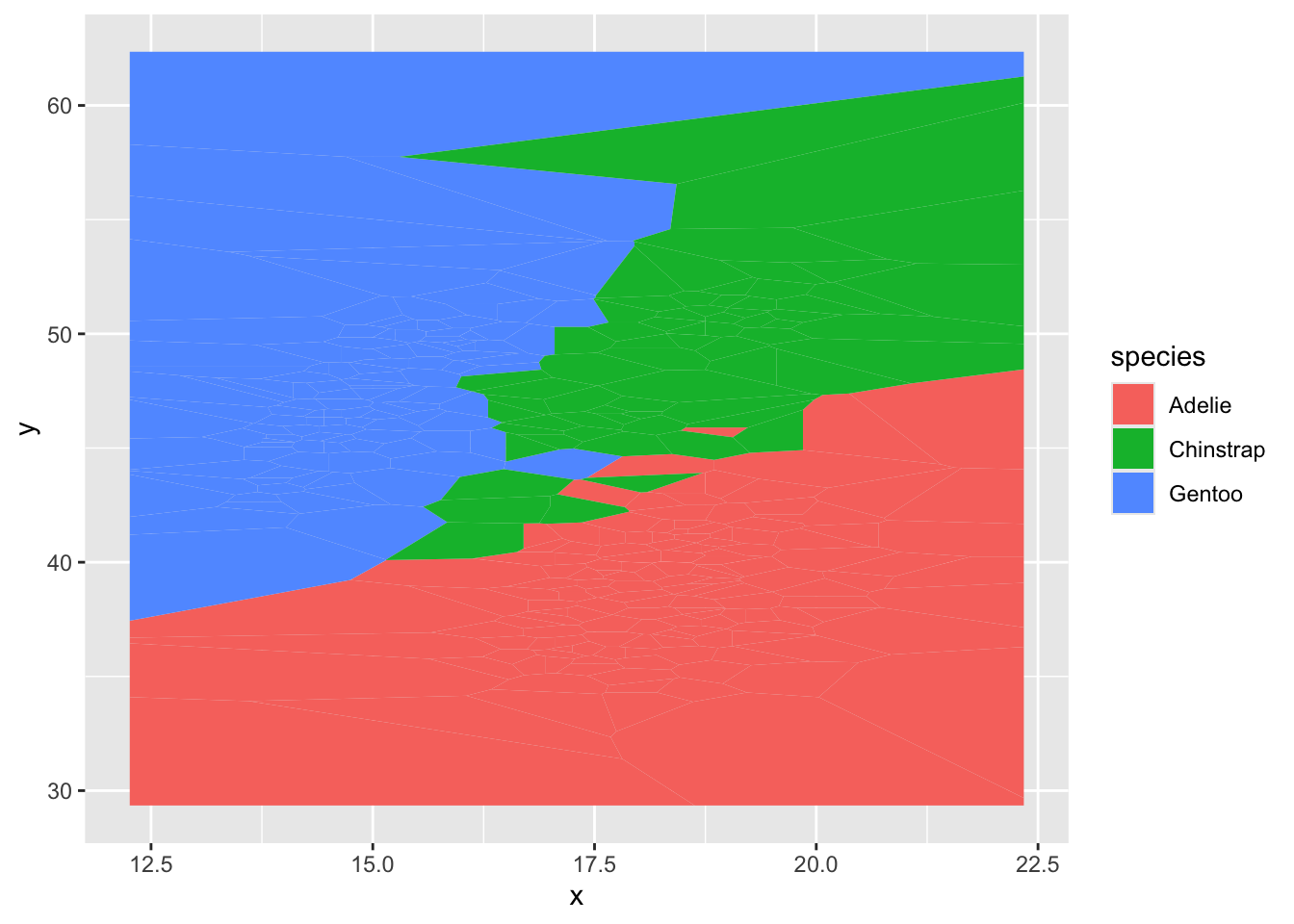
improve second
ggplot(d) + geom_voronoi(aes(x,y,fill = species),color = "grey")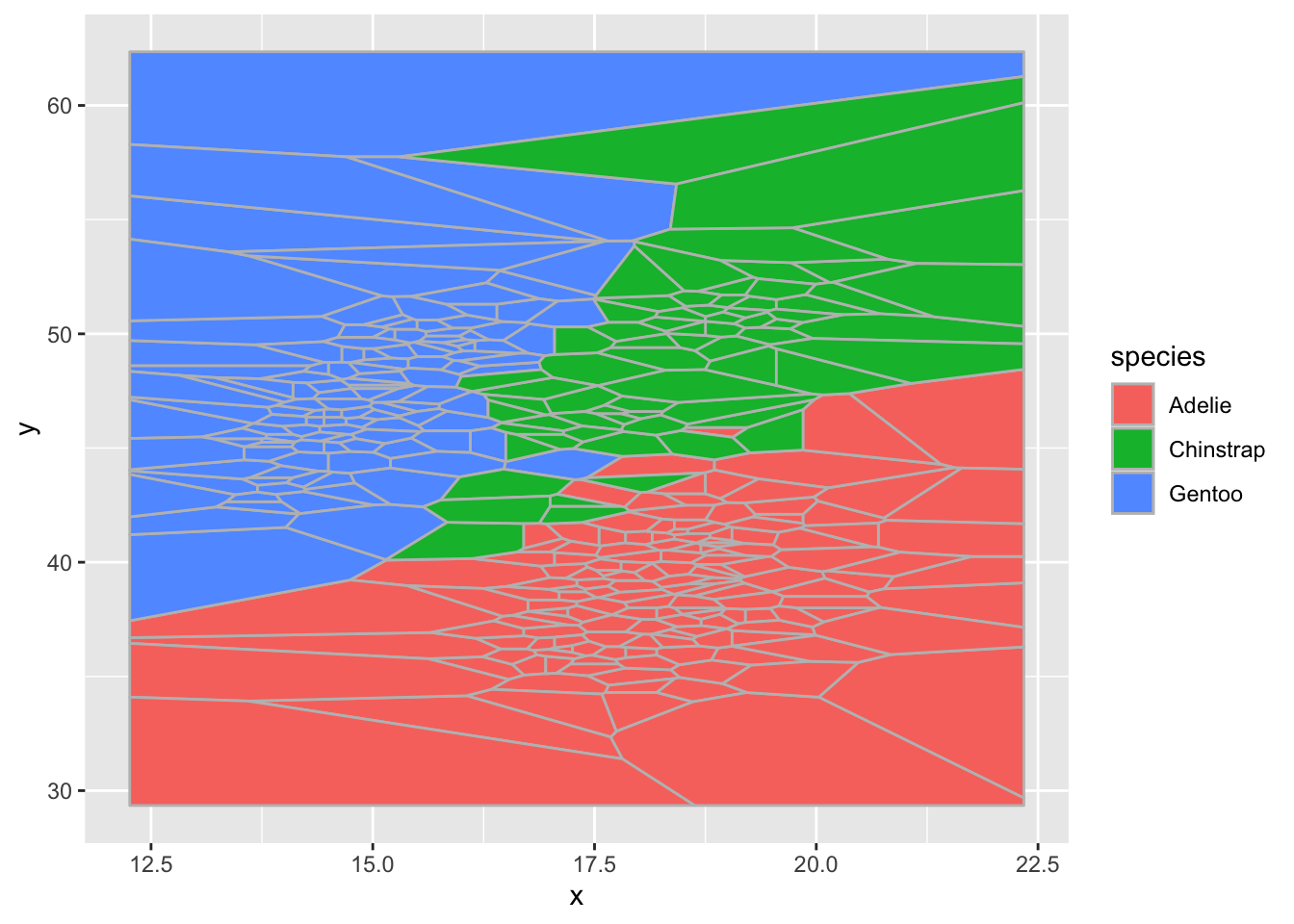
better second
ggplot(d,aes(x,y)) + geom_voronoi(aes(fill = species),
color = "grey", alpha = .4) +
geom_point(aes(color=species)) 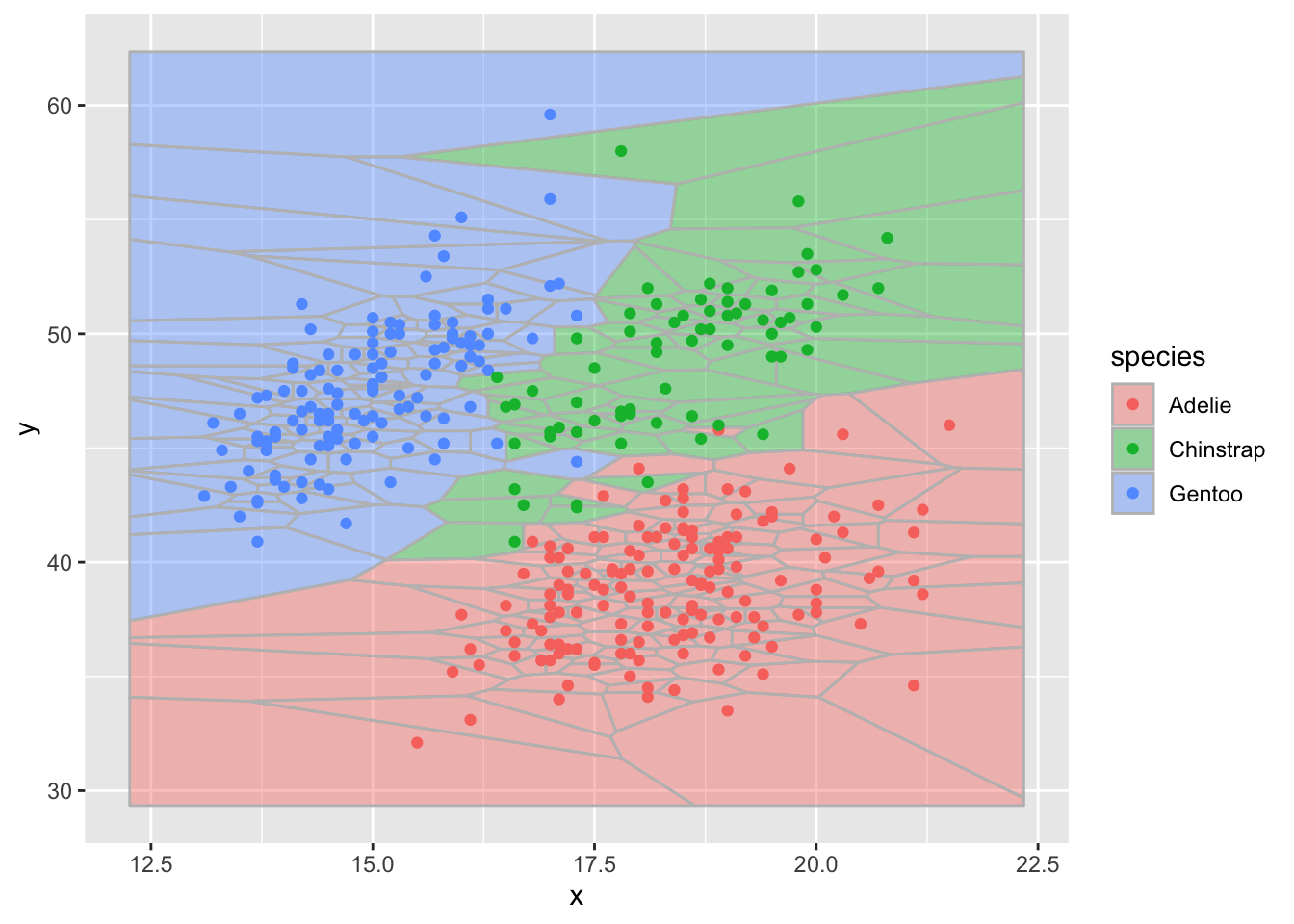
Use geom_voronoi_tile to work compactify tiles
ggplot(d,aes(x,y,group=-1L)) +
ggforce::geom_voronoi_tile(aes(fill = species), colour = 'black',
alpha = .4, max.radius = 2) +
geom_point(aes(color=species)) 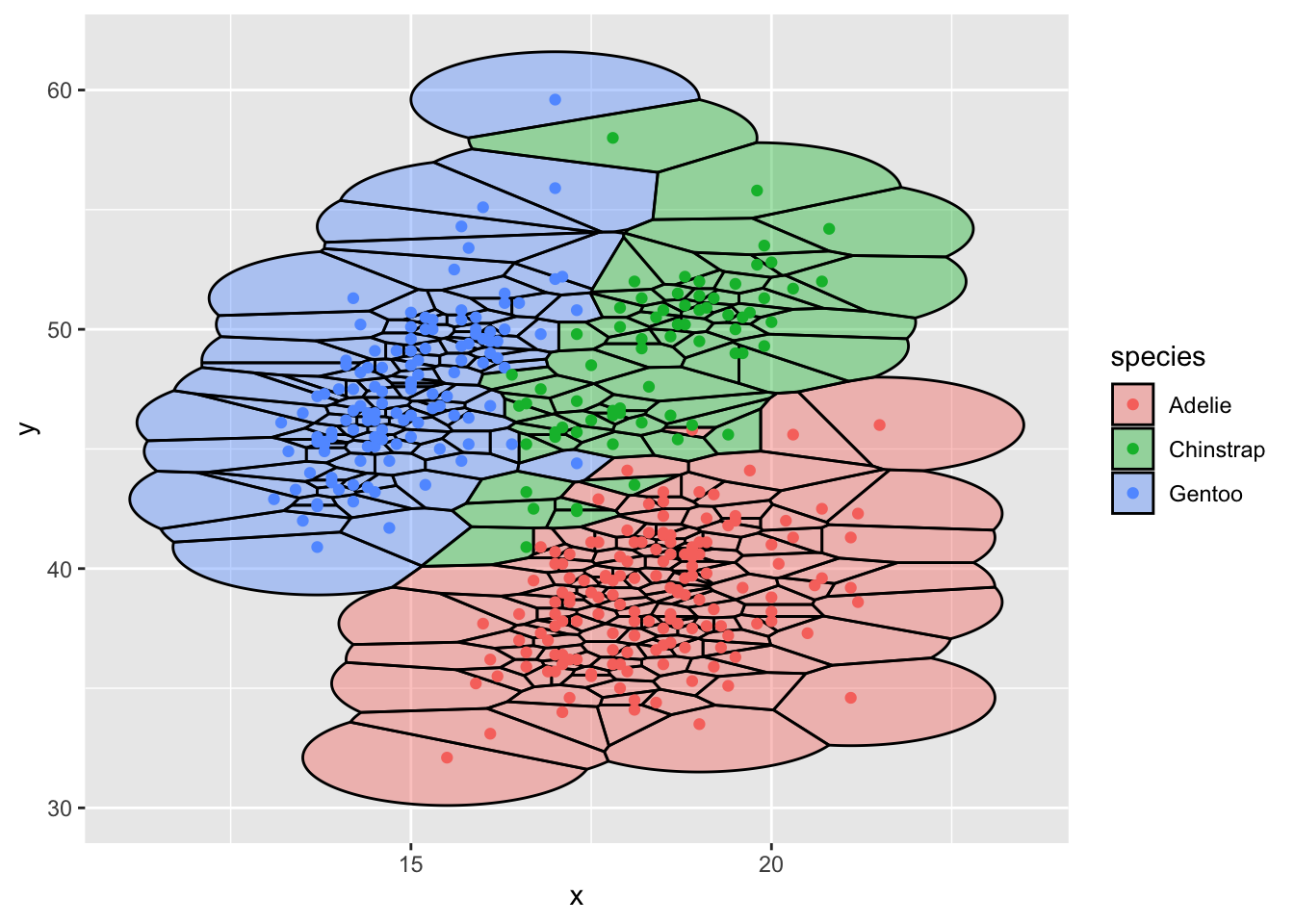
# zoom as usual
ggplot(d,aes(x,y,group=-1L)) +
ggforce::geom_voronoi_tile(aes(fill = species), colour = 'black',
alpha = .4, max.radius = 2) +
geom_point(aes(color=species)) +
scale_x_continuous(limits=c(16,20)) +
scale_y_continuous(limits=c(40,50)) 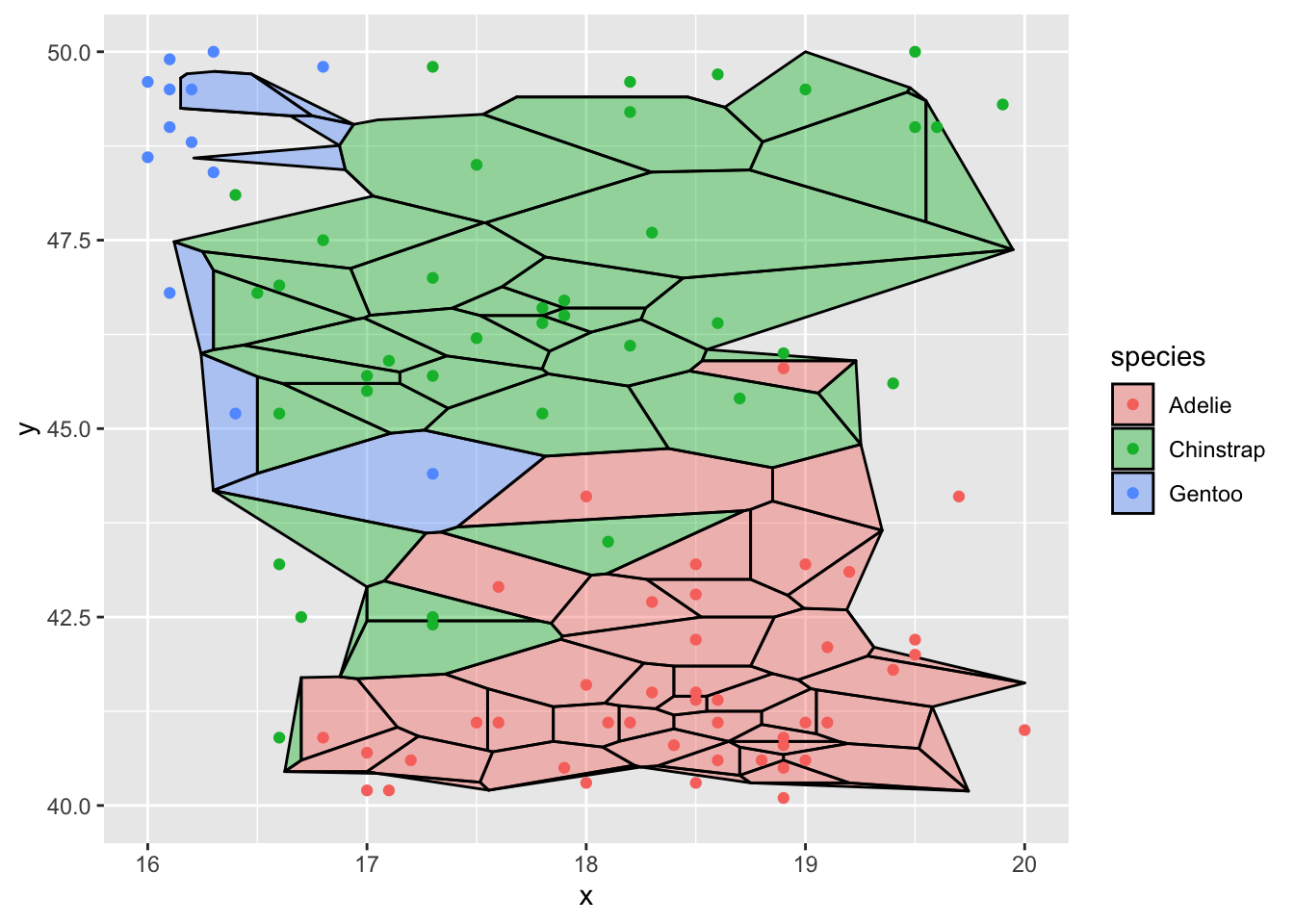
M A K E - B O U N D I N G - C I R C L E
Plot a large circle around the data to improve the edges of the voronoi diagram
get the mean of the data
mean_x <- mean(penguins$bill_depth_mm,na.rm=TRUE)
mean_y <- mean(penguins$bill_length_mm,na.rm=TRUE)range of data about mean
d <- d |> mutate(dist2mean = sqrt((y-mean_y)^2+(x-mean_x)^2))radius
rad <- max(d$dist2mean)
circle <- data.frame(x = mean_x+rad*cos(seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 25)),
y = mean_y+rad*sin(seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 25)),
group = rep(1,25))another approach to improving the edges
ggplot(d,aes(x,y,group=-1L)) +
geom_voronoi(
aes(fill = species), colour = 'black',alpha = .4,
outline = circle) +
geom_point(aes(color=species)) 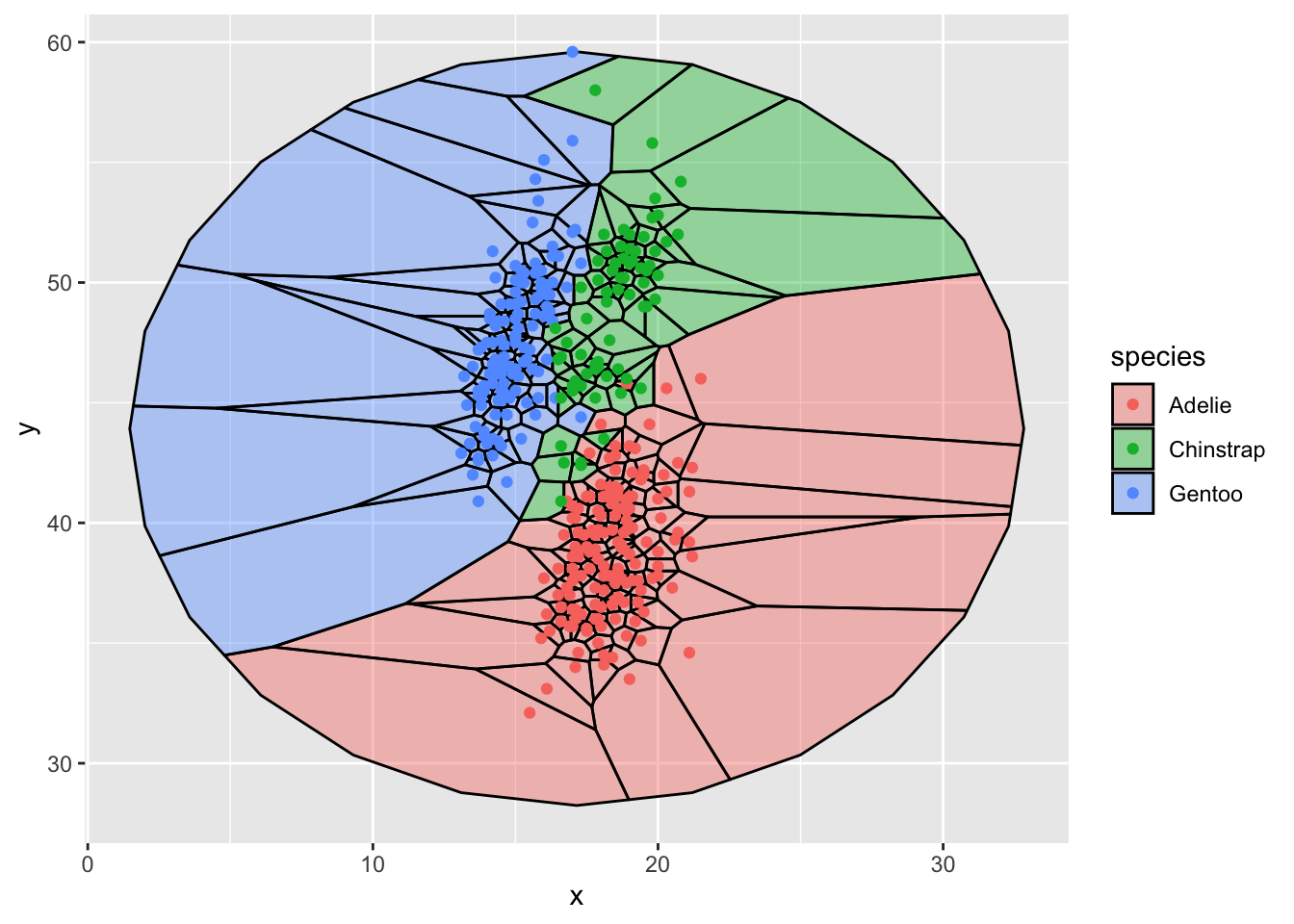
first voronoi diagram with circle outline
ggplot(d, aes(x,y)) +
stat_voronoi(geom="path", outline = circle) +
geom_point(aes(color = species))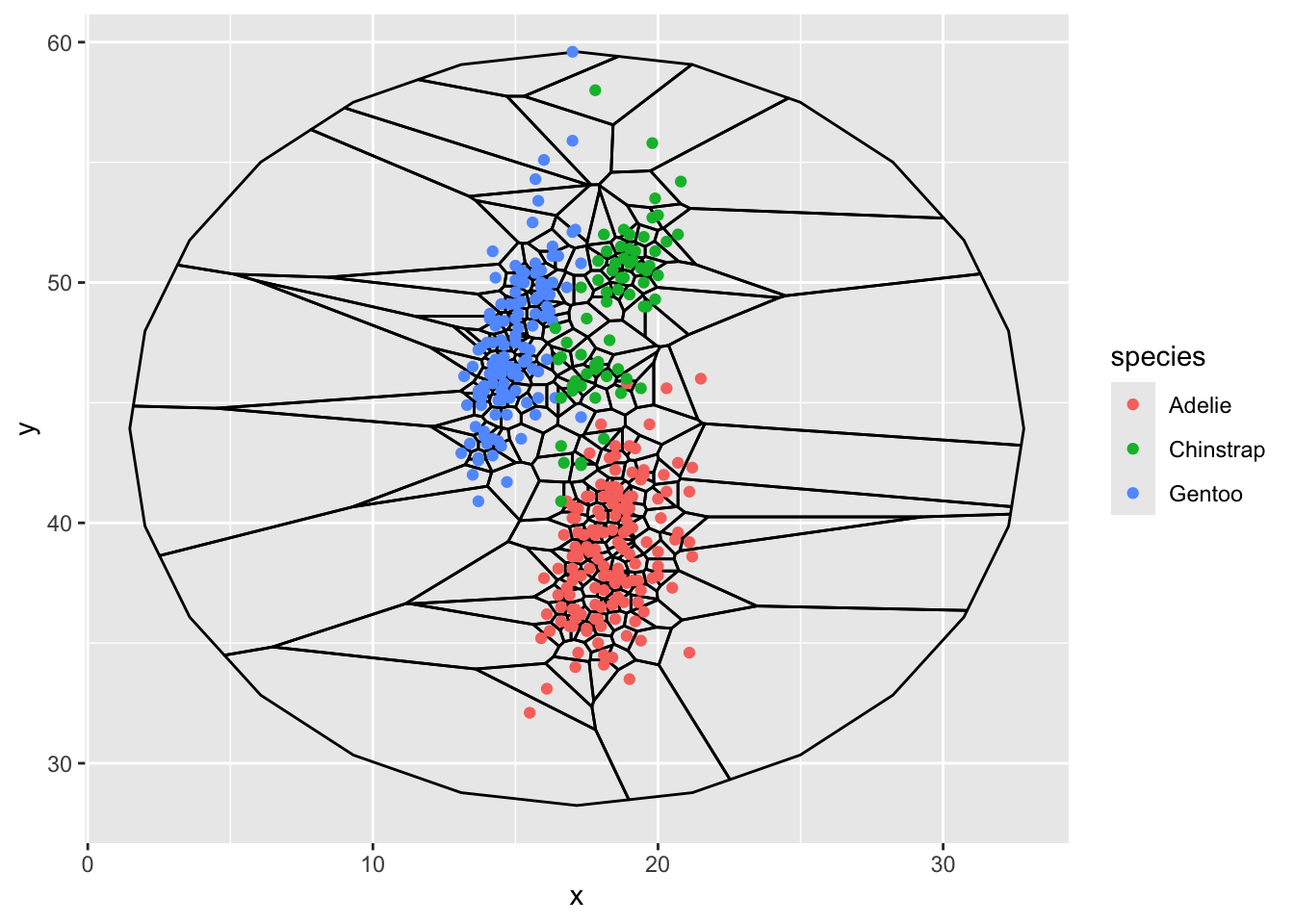
how could we use this to classify data
Suppose you find a new penguin with bill_depth = 15.3 and bill_length = 43.
What is the most likely species of this new penguin?
We can make a guess by looking at the graph.
newp <- tibble(x=15.3,y=43) # a new point
p <- ggplot(d, aes(x,y)) +
geom_voronoi(aes(fill=species),
outline = circle,
color = "grey") +
scale_fill_viridis_d(option = "D",alpha=.5) +
geom_point(aes(color=species)) +
scale_color_viridis_d(option = "H",alpha=.5) +
geom_point(data=newp,
mapping = aes(x,y),
shape = 7) +
scale_x_continuous(limits=c(12,25)) +
scale_y_continuous(limits=c(35,50))
p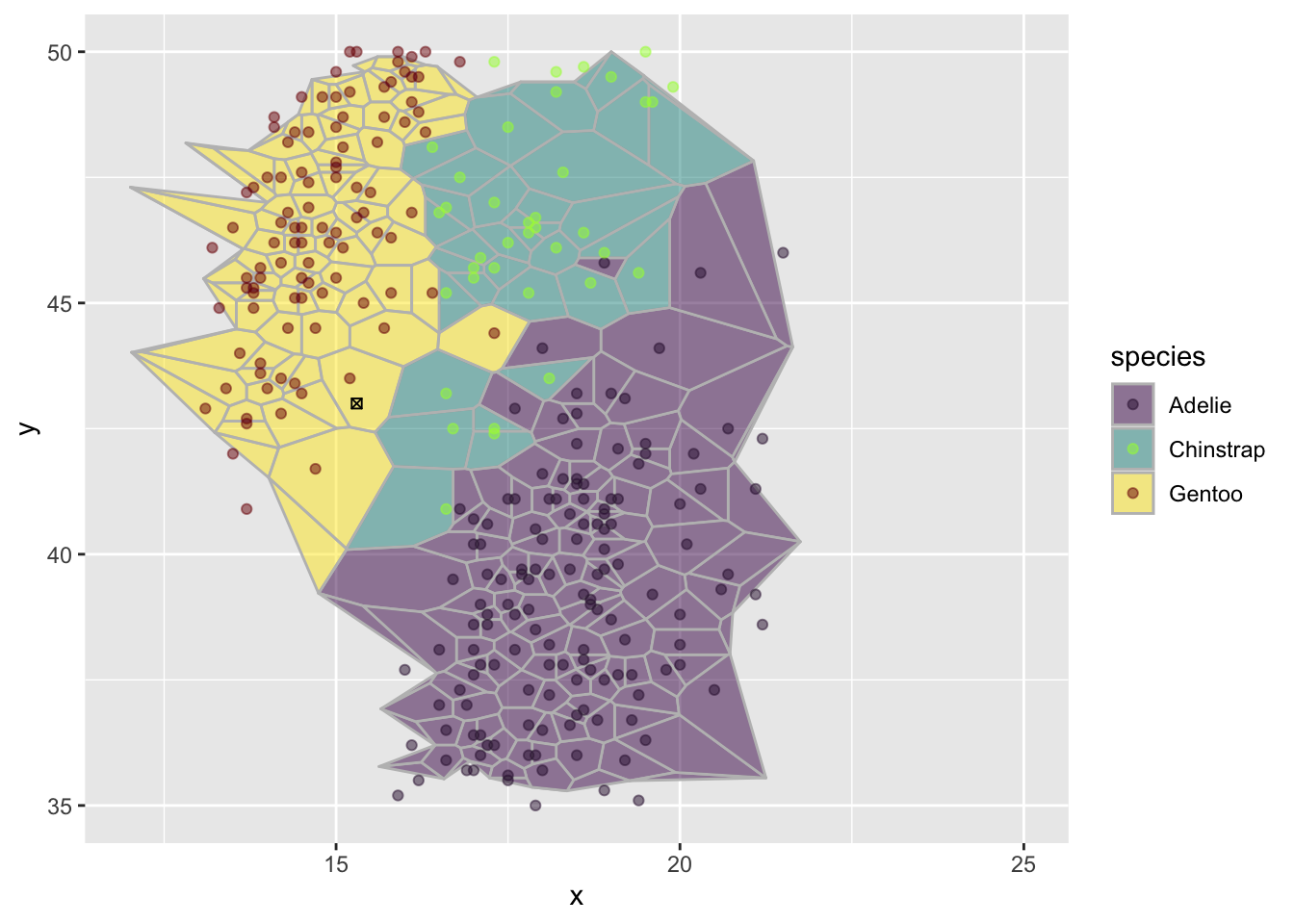
goal: compare new penguin to the centroid of each cell
create pts from raw data
Convert the x,y data into sf format
pts <- tibble(x = d$x, y = d$y, species = d$species) %>%
st_as_sf(coords = c('x', 'y')) %>%
st_set_crs(4326) turn circle data into sf format
cc <- select(circle,1:2) |> as.data.frame()
c_df <- st_as_sf(x = cc,coords = c("x", "y"), crs = "4326")voronoi of pts
vor <- st_voronoi(st_combine(pts))st_voronoi
st_voronoi returns a GEOMETRYCOLLECTION, and some plotting methods can’t use a GEOMETRYCOLLECTION.
this returns polygons instead
vor_poly <- st_collection_extract(vor)to put a bounding box around the sf data
box <- st_bbox(c_df) |> st_as_sfc()
vcrop <- st_crop(vor_poly, box)
plot(vcrop)compute centroid of each cell
cntrd1 <- vor_poly |> st_centroid()the coordinates of the centroid data
cntrd <- st_coordinates(cntrd1) |> as_tibble() |>
janitor::clean_names() |>
mutate(centroid_x = x, centroid_y = y)plot the centroids
p + geom_point(data=cntrd,aes(x,y),shape = 4) combine raw data and voronoi polygons
df <- cbind(pts,vor_poly) |> as_tibble() |>
rename(poly = geometry.1, point = geometry)combine voronoi polygons, the raw data and centroids
a <- cbind(df, cntrd) |> tibble() |> rename(geometry=poly)data containing the nearest centroid
nearest_cntrd <- mutate(cntrd,
d = sqrt((x-newp$x)^2 + (y-newp$y)^2)) |>
arrange(d) |> slice_head()the predicted species
filter(a,x==nearest_cntrd$x & y==nearest_cntrd$y) |> select(species)# A tibble: 1 × 1
species
<fct>
1 Adelie