Working with data inevitably leads to the need to filter out subsets, to sort data based on some rule and to find the unique observations. We often need to create new variables as modifications of existing ones. Some variables are often more important than others, thus we need to select them. Finally, renaming and moving variables to within view often makes working with data easier. The tools you learn here make all this possible.
Data Transformations
Row Functions
Column Functions
filter
mutate
arrange
select
distinct
rename
relocate
select
Row Functions
These functions change which rows are present in the data and keep the columns the same.
Filter observations based on conditions
Subset oberservations (rows) based on a logical condition.
This permutes the ordering of the rows. (Note the r in arrange, r for rows.) If you provide more than one column name, each additional column will be used to break ties in the values of preceding columns. To arrange in descending order use desc().
use where with is.factor(), or is.numeric(), or is.character()
starts_with("abc"): matches names that begin with “abc”.
ends_with("xyz"): matches names that end with “xyz”.
contains("ijk"): matches names that contain “ijk”.
num_range("x", 1:3): matches x1, x2 and x3.
To drop colummns: select(data,-c(this_col,that_col))
use regular expressions: select(matches("o.*u"))
Note: o.*u is a regular expression that matches an o followed by a u with any number of characters in between. country and population are returned because the names country and population each contain an o followed (at any distance) by a u.
Exercise
Use select() and these helper functions to create various subsets of penguins data.
---title: "Chapter 3: Row & Column Operations"toc-title: "arrange,distinct,mutate,select"date: "`r Sys.Date()`"toc: trueformat: html: code-overflow: wrap toc: true toc-title: "Table of Contents" # hide code? code-fold: true # link at top to globally unhide code code-tools: true # link functions used in code chunks to online docs code-link: trueexecute: warning: false message: false---Working with data inevitably leads to the need to filter out subsets, to sort data based on some rule and to find the unique observations. We often need to create new variables as modifications of existing ones. Some variables are often more important than others, thus we need to select them. Finally, renaming and moving variables to within view often makes working with data easier. The tools you learn here make all this possible.| Row Functions | Column Functions ||----------|---------:|| filter | mutate || arrange | select || distinct | rename || | relocate|| | select |: Data Transformations {.striped .hover}# Row FunctionsThese functions change which rows are present in the data and keep the columns the same. ## Filter observations based on conditions Subset oberservations (rows) based on a logical condition.Textbook link: [filter](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#arrange)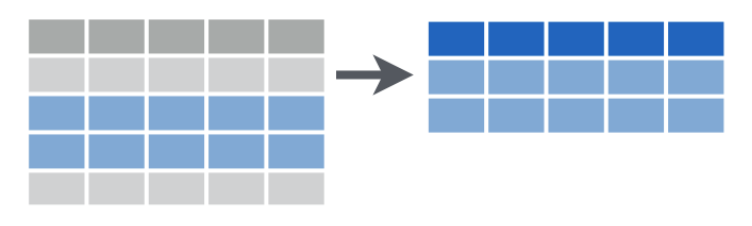{width=50%}## Arrange rows by value in ascending orderTextbook link: [arrange](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#arrange)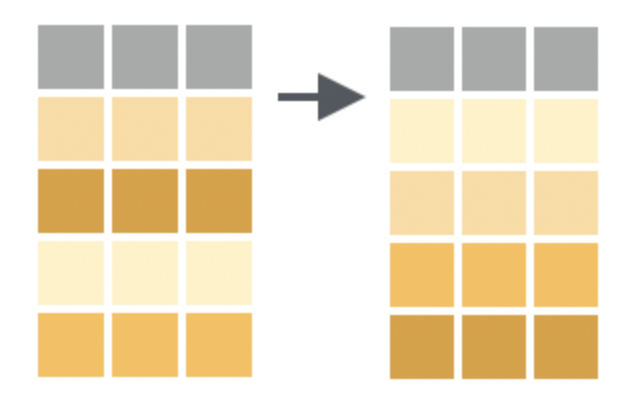{width=30%}This permutes the ordering of the rows. (**Note the r in arrange, r for rows.**) If you provide more than one column name, each additional column will be used to break ties in the values of preceding columns. To arrange in descending order use `desc()`.```{r}library(tidyverse)library(nycflights13)arrange(flights,month,dep_time)```## Keep distinct rows [](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#distinct)Use `distinct` on several column names to find unique combinations. The `.keep_all = TRUE` argument is used to retain all columsns```{r}library(nycflights13)flights |>distinct(origin,dest)```# Column functions ## Create new variables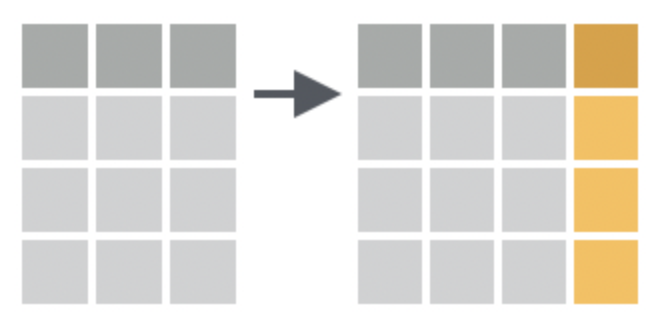{width=30%}Textbook link: [mutate](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#sec-mutate)Add new variables (columns), usually via a formula involving existing ones. Use these helper functions to relocate or newly created variables.(i) `.before = 1`(ii) `.after = some_var_name````{r mutate}library(palmerpenguins)penguins |> mutate(bill_num = bill_length_mm + bill_depth_mm, .before = 1)```## Select columns based on a logical testThis is useful if you have too many columns, choose which columns you wish to view.Textbook link: [select](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#sec-select)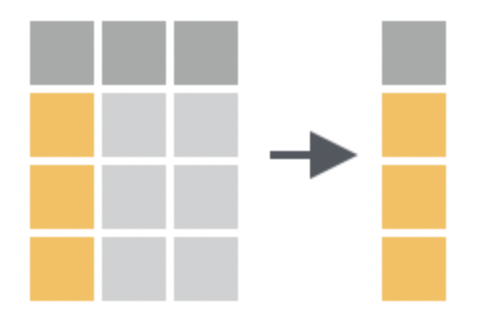{width=30%}### Select tips & helper functions i) use : to select a range ii) use ! to exclude iii) use `where` with `is.factor()`, or `is.numeric()`, or `is.character()` iv) `starts_with("abc")`: matches names that begin with “`abc`”. v) `ends_with("xyz")`: matches names that end with “`xyz`”. vi) `contains("ijk")`: matches names that contain “`ijk`”. vii) `num_range("x", 1:3)`: matches `x1, x2` and `x3`. viii) To drop colummns: `select(data,-c(this_col,that_col))` ix) use regular expressions: `select(matches("o.*u"))`Note: `o.*u` is a regular expression that matches an o followed by a u with any number of characters in between. country and population are returned because the names country and population each contain an o followed (at any distance) by a u.### ExerciseUse `select()` and these helper functions to create various subsets of penguins data.## [rename](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#rename)Explicitly rename variables. Do so in bulk with `janitor::clean_names`## [relocate](https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform#relocate)Permute the ordering of columns (notice the c in relocate, c for columns)You can also achieve this with `select()````{r eval=FALSE}relocate(penguins, sex, year)# versusselect(penguins, sex,year, everything())```# Assignment 5 Row verb exercises: <https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform.html#exercises>Column verb exercises: <https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform.html#exercises-1>