Chapter 3: Row & Column Operations
Working with data inevitably leads to the need to filter out subsets, to sort data based on some rule and to find the unique observations. We often need to create new variables as modifications of existing ones. Some variables are often more important than others, thus we need to select them. Finally, renaming and moving variables to within view often makes working with data easier. The tools you learn here make all this possible.
They are all contained in dplyr, which is included in the tidyverse, so as usual:
| Row Functions | Column Functions |
|---|---|
| filter | mutate |
| arrange | select |
| distinct | rename |
| relocate | |
| select |
Row Functions
These functions change which rows are present in the data and keep the columns the same.
Filter observations based on conditions
Subset oberservations (rows) based on a logical condition.
Textbook link: filter
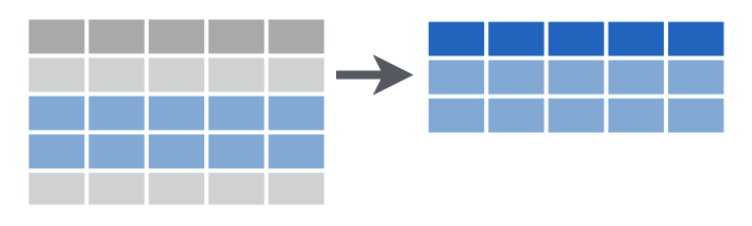
Arrange rows by value in ascending order
Textbook link: arrange
This permutes the ordering of the rows. (Note the r in arrange, r for rows.) If you provide more than one column name, each additional column will be used to break ties in the values of preceding columns. To arrange in descending order use desc().
Pipe to head() if you only want to see the first few results:
species island bill_len bill_dep flipper_len body_mass sex year
1 Adelie Dream 32.1 15.5 188 3050 female 2009
2 Adelie Dream 33.1 16.1 178 2900 female 2008
3 Adelie Torgersen 33.5 19.0 190 3600 female 2008
4 Adelie Dream 34.0 17.1 185 3400 female 2008
5 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475 <NA> 2007
6 Adelie Torgersen 34.4 18.4 184 3325 female 2007Code
species island bill_len bill_dep flipper_len body_mass sex year
1 Adelie Torgersen 34.6 21.1 198 4400 male 2007
2 Adelie Torgersen 33.5 19.0 190 3600 female 2008
3 Adelie Torgersen 35.1 19.4 193 4200 male 2008
4 Adelie Torgersen 37.3 20.5 199 3775 male 2009
5 Adelie Torgersen 38.6 21.2 191 3800 male 2007
6 Adelie Dream 39.2 21.1 196 4150 male 2007Keep distinct rows
Use distinct on several column names to find unique combinations. The .keep_all = TRUE argument is used to retain all columsns
Code
# this keeps all unique (origin, dest) pairs
library(nycflights13)
flights |> distinct(origin,dest) # A tibble: 224 × 2
origin dest
<chr> <chr>
1 EWR IAH
2 LGA IAH
3 JFK MIA
4 JFK BQN
5 LGA ATL
6 EWR ORD
7 EWR FLL
8 LGA IAD
9 JFK MCO
10 LGA ORD
# ℹ 214 more rows# A tibble: 224 × 2
origin dest
<chr> <chr>
1 EWR IAH
2 EWR ORD
3 EWR FLL
4 EWR SFO
5 EWR LAS
6 EWR PBI
7 EWR MIA
8 EWR ATL
9 EWR PHX
10 EWR MSP
# ℹ 214 more rowsColumn functions
Create new variables
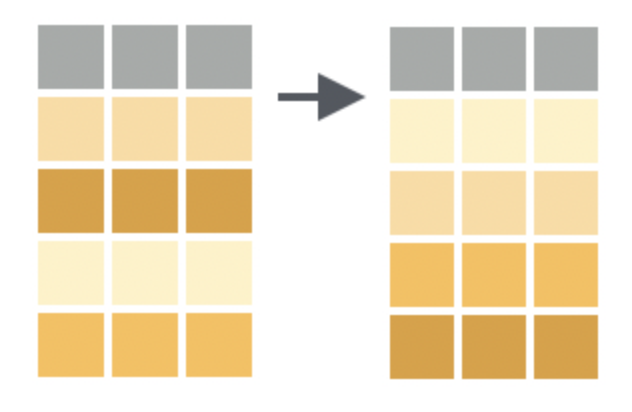
Textbook link: mutate
Add new variables (columns), usually via a formula involving existing ones. Use these helper functions to relocate or newly created variables.
.before = 1.after = some_var_name
Code
library(palmerpenguins)
penguins |> mutate(bill_ratio = bill_length_mm / bill_depth_mm, .after = island)# A tibble: 344 × 9
species island bill_ratio bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 2.09 39.1 18.7 181
2 Adelie Torgersen 2.27 39.5 17.4 186
3 Adelie Torgersen 2.24 40.3 18 195
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 1.90 36.7 19.3 193
6 Adelie Torgersen 1.91 39.3 20.6 190
7 Adelie Torgersen 2.19 38.9 17.8 181
8 Adelie Torgersen 2 39.2 19.6 195
9 Adelie Torgersen 1.88 34.1 18.1 193
10 Adelie Torgersen 2.08 42 20.2 190
# ℹ 334 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: body_mass_g <int>, sex <fct>, year <int>Select columns based on a logical test
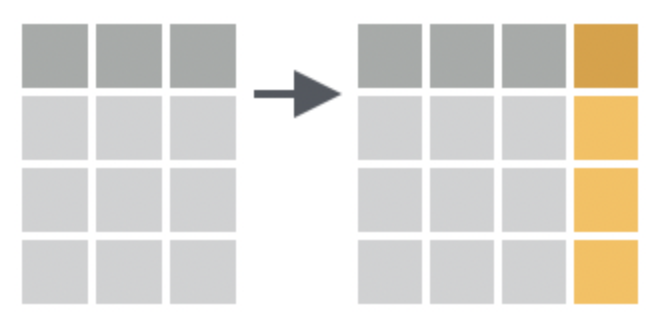
This is useful if you have too many columns, choose which columns you wish to view.
Textbook link: select
Select tips & helper functions
- use : to select a range
- use ! to exclude
- use
wherewithis.factor, oris.numeric, oris.character -
starts_with("abc"): matches names that begin with “abc”. -
ends_with("xyz"): matches names that end with “xyz”. -
contains("ijk"): matches names that contain “ijk”. -
num_range("x", 1:3): matchesx1, x2andx3. - To drop colummns:
select(data,-c(this_col,that_col)) - use regular expressions:
select(matches("^b.*mm"))
Note: ^b.*mm is a regular expression that matches a b followed by anything . any number times * followed by mm. See regex101.com
Exercise
Use select() and these helper functions to create various subsets of penguins data.
rename
Explicitly rename variables. Do so in bulk with janitor::clean_names
relocate
Permute the ordering of columns (notice the c in relocate, c for columns)
You can also achieve this with select()
Code
relocate(penguins, sex, year)
# versus
select(penguins, sex,year, everything())Assignment 5: Due 9/16
Row verb exercises: https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform.html#exercises
Column verb exercises: https://r4ds.hadley.nz/data-transform.html#exercises-1