library(tidyverse)
library(tidyquant) # contains coord_x_datetime for dates as coordinates
library(scales)Load & Wrangle Zillow Data
Intro loops & functions
Library load
This data, from Zillow, comes to us in two files; one associated with selling price and one with listing price. We well join the datasets together so that each house is an observation and list price and sell price are variables.
0. load data
sell <- read_csv("https://euclid.nmu.edu/~joshthom/teaching/dat309/week7/Metro_invt_fs_uc_sfrcondo_sm_month_sell_f25.csv") |> janitor::clean_names()
list <- read_csv("http://euclid.nmu.edu/~joshthom/teaching/dat309/week7/Metro_median_sale_price_now_uc_sfrcondo_month_sold_f25.csv") |> janitor::clean_names()
print(sell, n = 5)# A tibble: 928 × 95
region_id size_rank region_name region_type state_name x2018_03_31 x2018_04_30
<dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 102001 0 United Sta… country <NA> 1421529 1500195
2 394913 1 New York, … msa NY 73707 80345
3 753899 2 Los Angele… msa CA 21998 23784
4 394463 3 Chicago, IL msa IL 38581 42253
5 394514 4 Dallas, TX msa TX 24042 25876
# ℹ 923 more rows
# ℹ 88 more variables: x2018_05_31 <dbl>, x2018_06_30 <dbl>, x2018_07_31 <dbl>,
# x2018_08_31 <dbl>, x2018_09_30 <dbl>, x2018_10_31 <dbl>, x2018_11_30 <dbl>,
# x2018_12_31 <dbl>, x2019_01_31 <dbl>, x2019_02_28 <dbl>, x2019_03_31 <dbl>,
# x2019_04_30 <dbl>, x2019_05_31 <dbl>, x2019_06_30 <dbl>, x2019_07_31 <dbl>,
# x2019_08_31 <dbl>, x2019_09_30 <dbl>, x2019_10_31 <dbl>, x2019_11_30 <dbl>,
# x2019_12_31 <dbl>, x2020_01_31 <dbl>, x2020_02_29 <dbl>, …print(list, n = 5) # A tibble: 396 × 216
region_id size_rank region_name region_type state_name x2008_02_29 x2008_03_31
<dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 102001 0 United Sta… country <NA> 170600 175000
2 394913 1 New York, … msa NY 400000 390000
3 753899 2 Los Angele… msa CA 470000 455000
4 394463 3 Chicago, IL msa IL 219000 220000
5 394514 4 Dallas, TX msa TX 138000 145456
# ℹ 391 more rows
# ℹ 209 more variables: x2008_04_30 <dbl>, x2008_05_31 <dbl>,
# x2008_06_30 <dbl>, x2008_07_31 <dbl>, x2008_08_31 <dbl>, x2008_09_30 <dbl>,
# x2008_10_31 <dbl>, x2008_11_30 <dbl>, x2008_12_31 <dbl>, x2009_01_31 <dbl>,
# x2009_02_28 <dbl>, x2009_03_31 <dbl>, x2009_04_30 <dbl>, x2009_05_31 <dbl>,
# x2009_06_30 <dbl>, x2009_07_31 <dbl>, x2009_08_31 <dbl>, x2009_09_30 <dbl>,
# x2009_10_31 <dbl>, x2009_11_30 <dbl>, x2009_12_31 <dbl>, …1. rename x’s with sell and list, respectively
First, we rename variables to make it easier to interpret the list & sell price variables. We have rename_with use the str_replace function to perform a renaming of many variables at once.
- The
~syntax makesstr_replaceinto a function whose argument. - The data is sent to the
.spot.
- Thy syntax is str_replace(data, thing_to_replace, new_string)
sell <- sell |> rename_with(~str_replace(.,"x","sell_"))
list <- list |> rename_with(~str_replace(.,"x","list_"))2. use names() and head() to note the 1st 10 variables
list |> names() |> head(n=10) [1] "region_id" "size_rank" "region_name" "region_type"
[5] "state_name" "list_2008_02_29" "list_2008_03_31" "list_2008_04_30"
[9] "list_2008_05_31" "list_2008_06_30"sell |> names() |> head()[1] "region_id" "size_rank" "region_name" "region_type"
[5] "state_name" "sell_2018_03_31"3. Joining 101:
There are several ways of joining two data sets together, some are illustrated below.
join two data sets with full_join
Joining two data frames using “left_join” or “right_join” requires a variable common to both data frames and keeps data. We use full_join to bring in new (non-redundant) variables.
Learn more about joining here.
list_sell <- full_join(sell,list)5. pivot to get plotable data
#
# selling price & listing price are variables
zillow <- pivot_longer(list_sell,
cols = starts_with("sell"),
names_to = "sell_date",
values_to = "sell_price") |>
pivot_longer(
cols = starts_with("list"),
names_to = "list_date",
values_to = "list_price")
zillow <- zillow |>
mutate(
list_date = as_datetime(str_remove(list_date,"list_")),
sell_date = as_datetime(str_remove(sell_date,"sell_"))
) |>
relocate(list_date,.before=1)7. filter to get some reasonable sized data
# parameter "name" : vector of strings of state names: c("CO","MI")
# parameter "number" : the number of regions to pull from each states
get_states <- function(name, number){
# empty dataset
d <- {}
for (i in 1:length(name)){
# print the name of the state for sanity
print(name[i])
# get all data for the given name
my_states <- filter(zillow, state_name %in% name[i])
# grab a few region_names from each state
some_names <- distinct(my_states,region_name) |>
slice_sample(n = number)
some_regions <- filter(my_states,
region_name %in% pull(some_names))
# could also do some_names[[1]] to extract the vector from the tibble
d <- bind_rows(d,some_regions)
}
return(d)
}
zil_sub <- get_states(c("CO","MI","AL","FL"),3)[1] "CO"
[1] "MI"
[1] "AL"
[1] "FL"8. plot prices for each region
p <- ggplot(zil_sub, aes(x = sell_date, y = sell_price,
group = region_name,
color = region_name)) + geom_line()
print(p)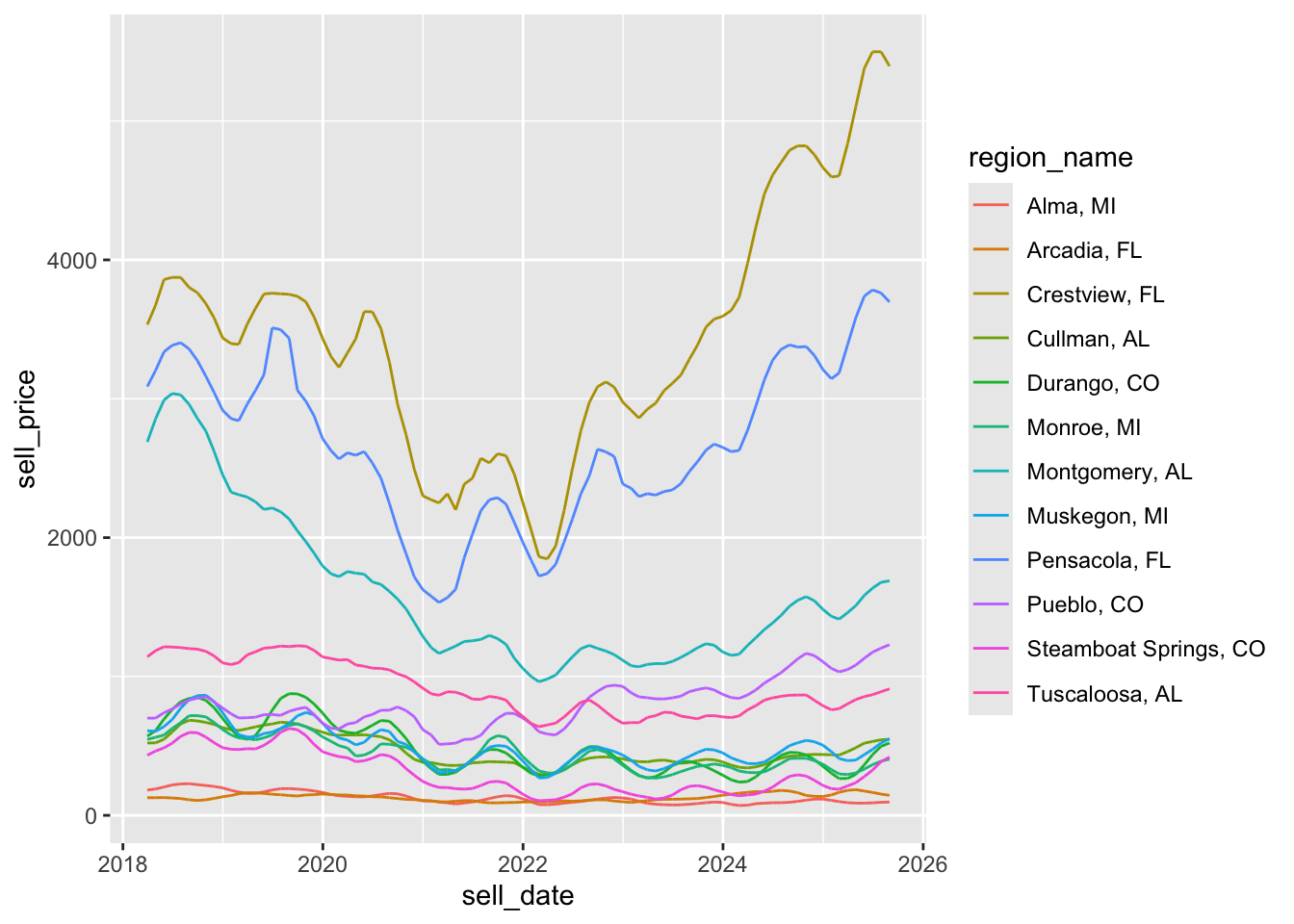
9. Plot list prices for each region
# option 1: plot alongside the sell plot
q <- ggplot(zil_sub, aes(x = list_date, y = list_price,
group = region_name,
color = region_name)) + geom_line()
print(q)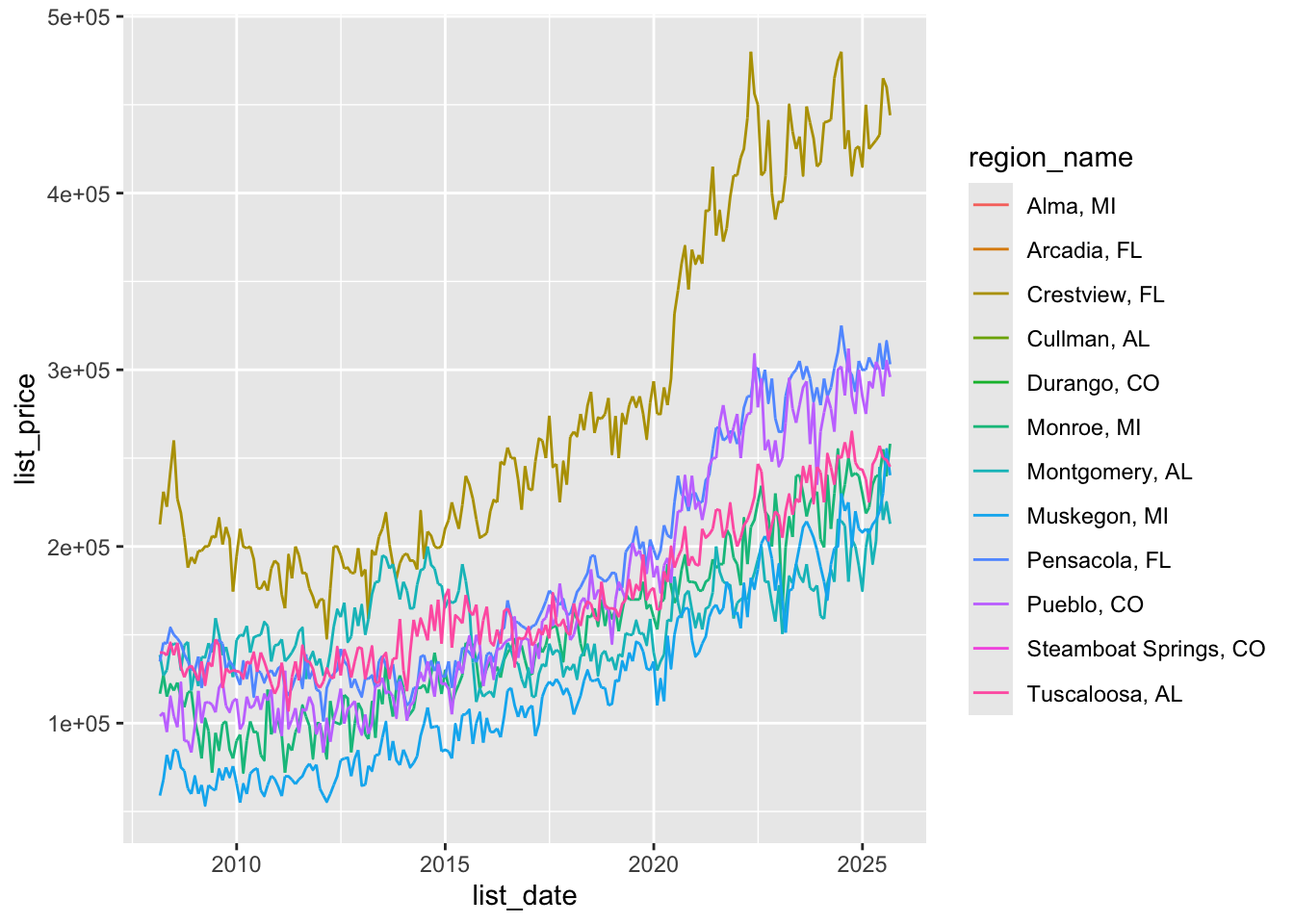
This works better:
zz <- mutate(zil_sub,
sell_date = as_date(sell_date),
list_date = as_date(list_date))
p <- ggplot(zz, aes(x = sell_date, y = sell_price,
group = region_name,
color = region_name)) +
# below, we draw solid lines for selling prices
geom_line(linetype = 1) +
geom_line(aes(x = list_date, y = list_price,
group = region_name,
color = region_name), linetype = 2)This is even better:
# zoom to the interesting region
p + scale_x_date(date_breaks = "2 years")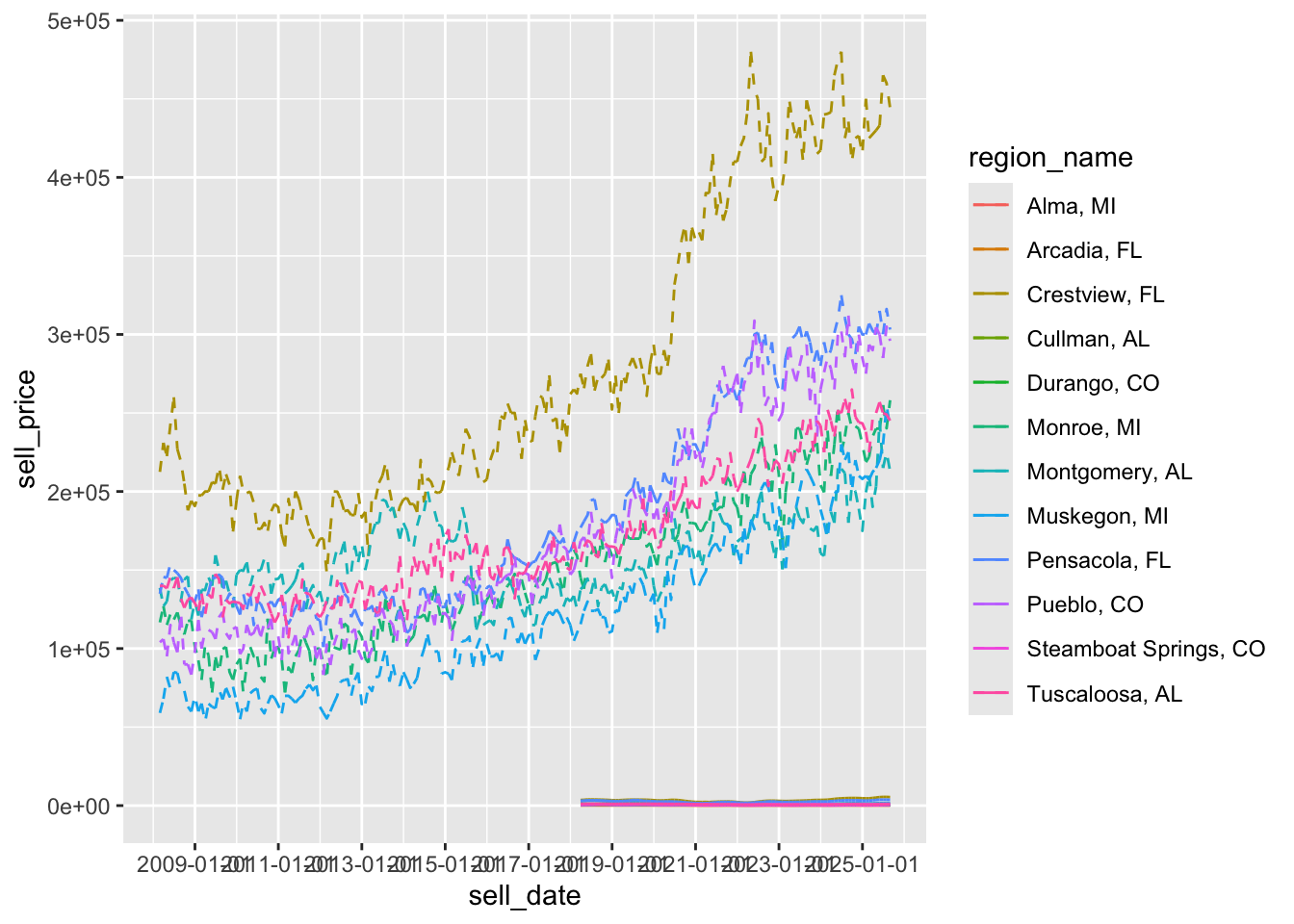
#p + coord_x_datetime(xlim = c("2018-01-01", "2023-12-31")) # even better still
p + scale_x_date(date_breaks = "1 year", date_labels= "%Y")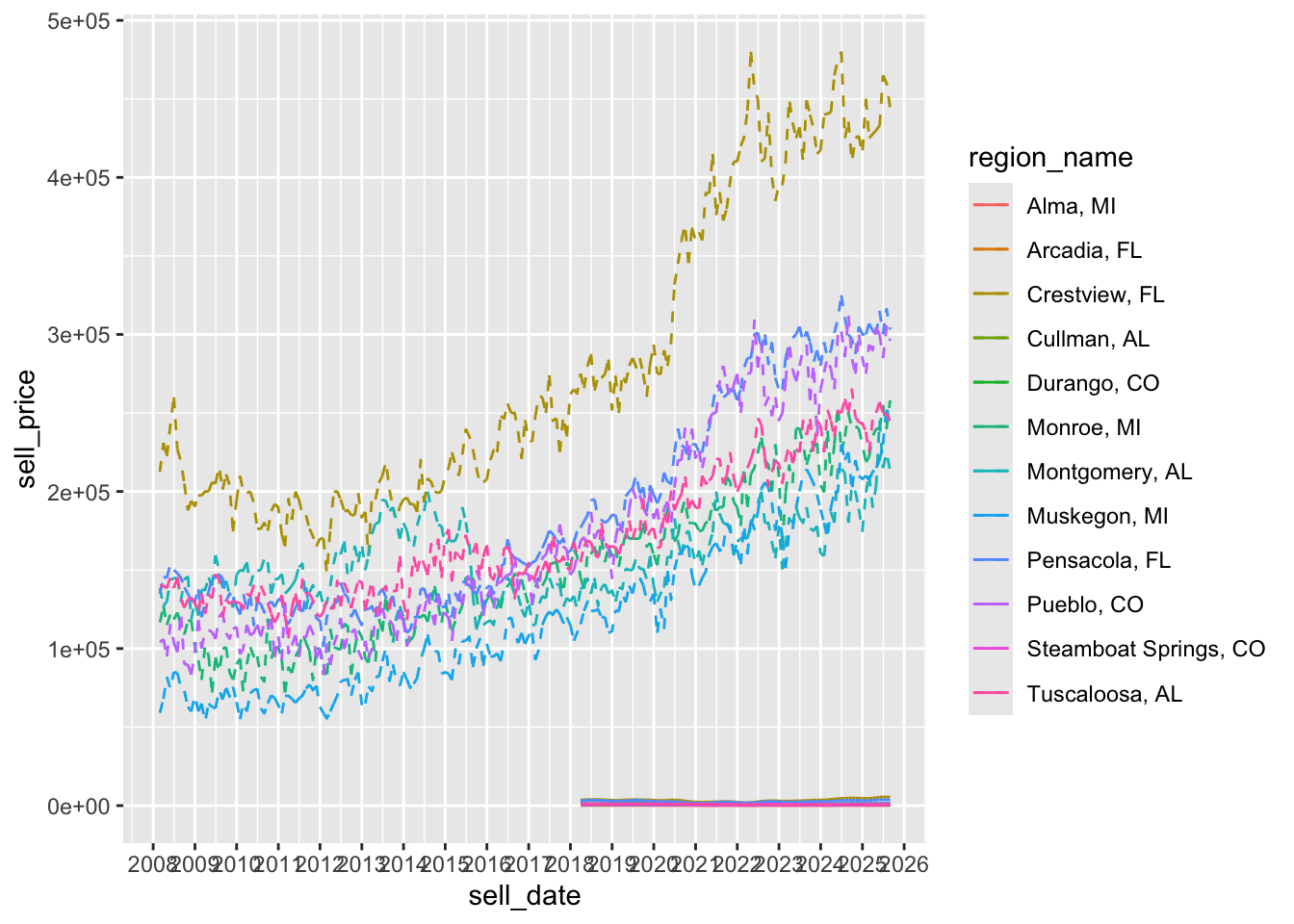
Zoom in on post 2018. Here we use coord_x_date to showcase how to zoom without losing data. (The coord_ functions allow for zooming without removing data that might be used to compute a statistic)
p + scale_x_date(
date_breaks = "1 year",
date_labels= "%Y") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 5)) +
coord_x_date(xlim = c("2018-01-01","2024-01-01"))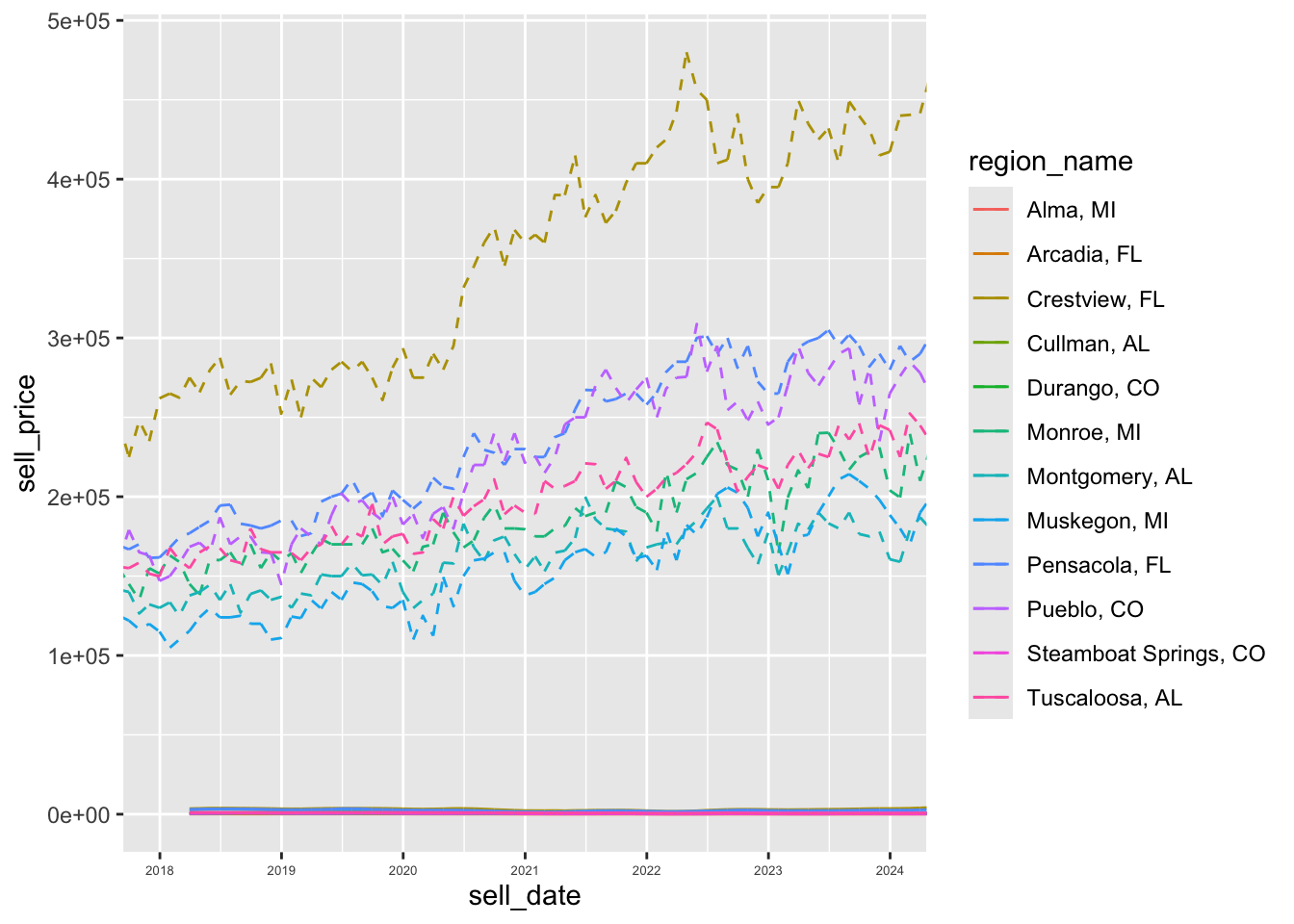
Get better formatting on the y-axis
p + scale_x_date(
date_breaks = "1 year",
date_labels= "%Y") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 5)) +
scale_y_continuous(label = label_dollar(prefix = "$"))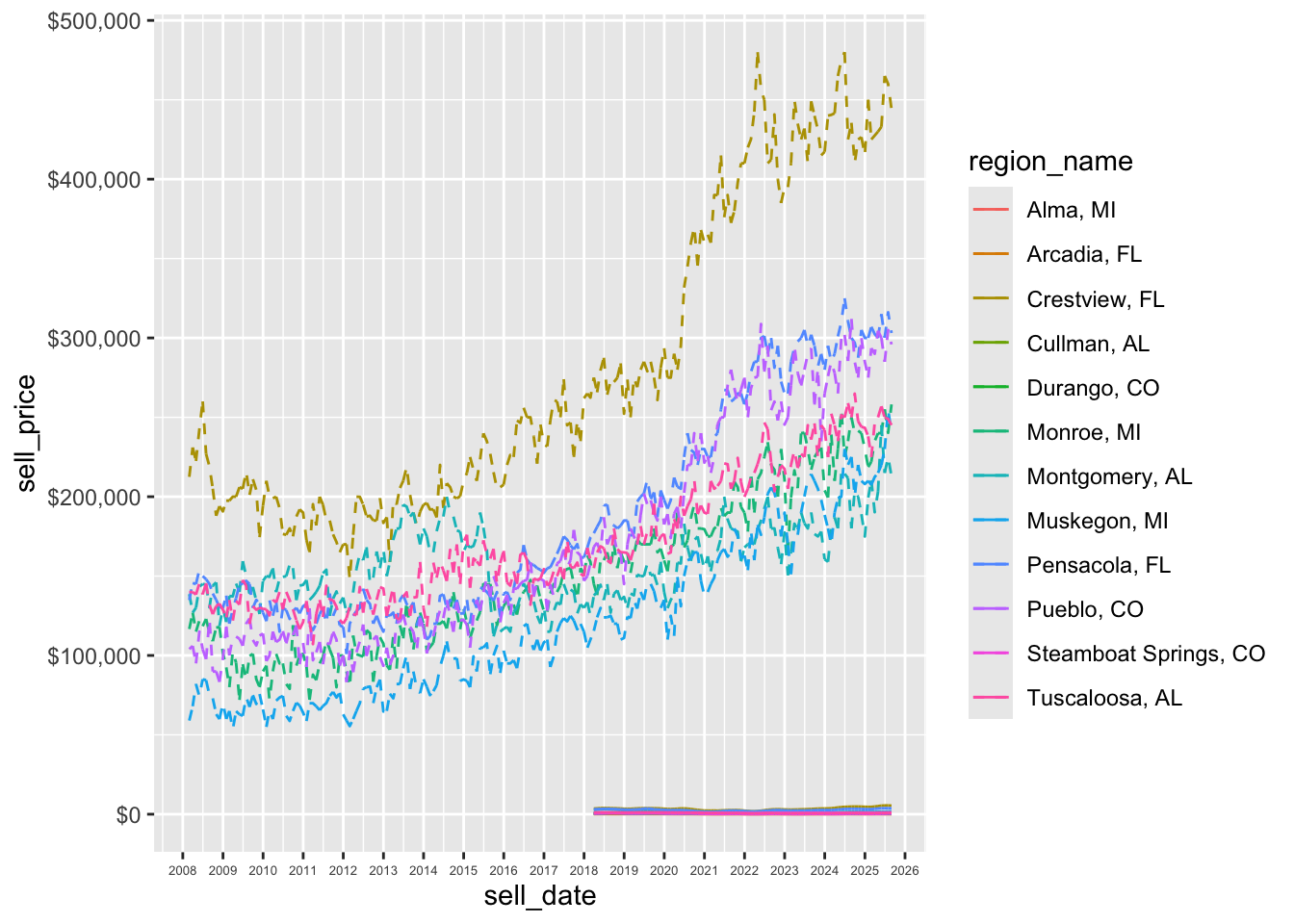
10. zoom to the interesting region
p + scale_x_date(
date_breaks = "1 year",
date_labels= "%Y",
limits =
c(as_date("2018-01-01"), as_date("2023-12-31"))) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 5)) +
scale_y_continuous(label = label_dollar(prefix = "$")) +
labs(title = "Selling Price vs. Listing Price",
subtitle = "Dotted line is listing price and solid line is selling price")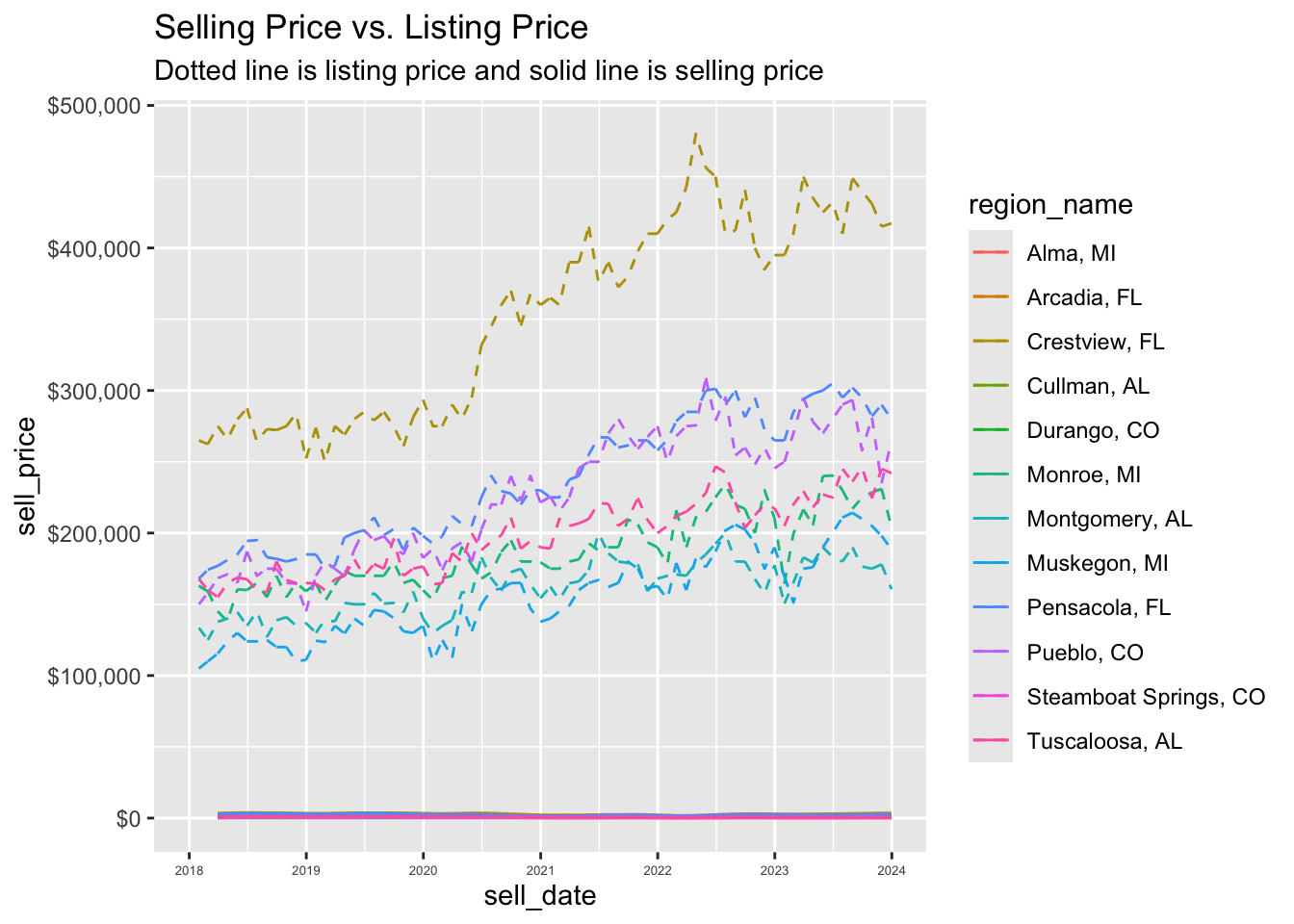
Save data for future work
This saves the variable zil_sub to the filename indicated below. Load it back up in R with load("zillow-data.Rdata").
write_rds(zil_sub, file = "~/t/dat309/week7/zillow-data.Rdata")